(How) do network operators use/contribute to/$upport open source software? The final report from the pilot project and survey are available in whole or in part: https://possie.techark.org/all-the-details-network-operators-oss-study/ .
-
Recently on TechArk
 Recently on URSA
Recently on URSA- Mind Your MANRS!The Internet Society has been working on Mutually Agreed Norms for Routing Security (MANRS) for a few years, and they recently funded some industry research to gain insights into network operators’ and enterprises’ requirements and plans around routing security. The … Continue reading →
- Routing security: work with what you’ve got!It seemed like there would be little appetite for discussing next steps in routing infrastructure authentication and verification after the DDoS attack on Dyn (October 2016), when it became clear that large scale attacks are feasible without spoofing IP addresses, … Continue reading →
- Necessary… but not sufficient: Are we on the right track for Internet security?Last Wednesday, in the hallways of the NANOG 68 meetings in Dallas, I started asking a question that goes to the heart of prioritizing work to improve Internet security; on Friday, with the DDoS attack on Dyn’s infrastructure, we got … Continue reading →
- Routing Security — why trust information?Trust is in the eye of the beholder – but it has to be based on something. In different contexts, crypto may be more relevant than heuristics, and vice versa. Traditionally, in Internetworking, business relationships have had a big role … Continue reading →
- Mind Your MANRS!
 Recently on NOMA
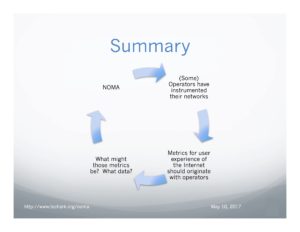
Recently on NOMA- NOMA: Static snapshot and nextsA while back, I wrote a guest blog for APNIC on the topic of the first results from the NOMA pilot work with RIPE NCC’s Atlas framework. I concluded: “Nevertheless, while these results are pretty preliminary, they do highlight the … Continue reading →
- Data! NOMA gets air (time) in BudapestToday I had the opportunity to talk to the RIPE meeting crowd about my use of the RIPE NCC Atlas measurements infrastructure to simulate the NOMA v6 health metric measurement. NOMA is based on operators instrumenting their networks. The RIPE … Continue reading →
- NOMA Measurements Template (Media)This is the persistent reference page for the NOMA Measurements Template document. Please use this page’s URL to refer to the document: http://www.techark.org/noma-measurements-template/ Current version of the document: http://www.techark.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/20161208-NOMA-Measurements-Template.pdf
- Internet Measurements Landscape (2016): Systems, Approaches and a Comparative Framework (Media)This is the persistent reference page for the Internet Measurements Landscape (2016) paper. Please use this page’s URL to refer to the paper (http://www.techark.org/internet-measurements-landscape-2016-systems-approaches-and-a-comparative-framework). Current version of the document: http://www.techark.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/20161213-NOMA-SurveyPaper.pdf
- 2016 NOMA Vision Paper (Media)This is the persistent reference page for the 2016 NOMA Vision Paper. Please use this page’s URL to refer to the paper: http://www.techark.org/2016-noma-vision-paper/ Current version of the document: http://www.techark.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/20161209-NOMA-Vision-Paper-RefUpdate.pdf (Updated URL for reference to Internet Measurements Survey paper) Older … Continue reading →
- NOMA: Static snapshot and nexts
TechArk Archives
Categories